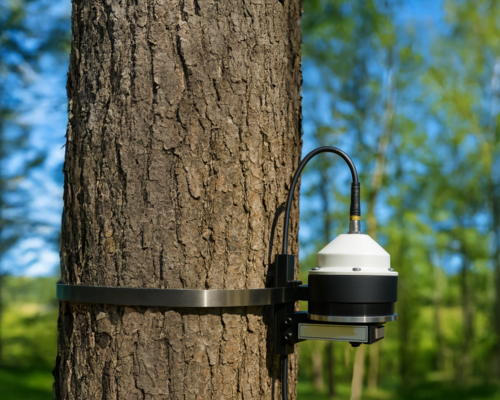
Four researchers from the OdinS R&D department (Rafael Marín, Jesús Sánchez, Jorge Gallego and Alejandro Arias) have published a new paper that proposes an innovative approach to improve energy efficiency in secure communication of IoT devices deployed in environments with limited connectivity, such as Smart Agriculture and Smart Cities .
The study explores the joint implementation of EDHOC (Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman Over COSE) , a lightweight key exchange protocol that ensures secure communications on resource-constrained devices, together with SCHC (Static Context Header Compression) , a protocol designed to compress and fragment data packets. In addition, LoRaWAN is used as a communication protocol, enabling efficient data transmission on low-power, long-range networks.
The combined use of EDHOC and SCHC is an innovative proposal, and the results obtained in the research are promising:
✅ Up to 54% compression in the size of EDHOC messages thanks to SCHC, reducing the amount of data transmitted.
✅ 20% reduction in energy consumption , since the LoRa module connected to the IoT device transmits for less time.
✅ Longer lifespan of IoT devices and lower environmental footprint .
This breakthrough represents a step forward in the development of efficient and sustainable IoT solutions in environments with connectivity restrictions, optimising both the security and energy consumption of devices.
The paper is available for a limited time at this link .